On the 20th of October a tropical depression formed in the Eastern Pacific, well south of Mexico and began drifting slowly northwest into an area of warm sea surface temperatures (SST’s) of about 30°C with low shear.
[map type=”terrain” autofit=”1″ disable_scrollwheel=”1″] [pin]Cuixmala[/pin] [pin tooltip=”La Manzanilla”]Selva de Melaque[/pin] [pin]Puerto Vallarta[/pin] [/map]Typically hurricanes of this strength are not seen this late in the Eastern Pacific, but very warm SST’s were still present in the area – perhaps influenced by the strong El Niño that is ongoing, provided the fuel necessary for a hurricane of this strength. After drifting northwest without significant intensification early in the week, Thursday is when Patricia began intensifying as it produced a large burst of convection. Patricia intensified to a rate the Western Hemisphere had not seen before – it dropped an incredible 100mb within 24 hours, and at the same time Patricia reached category five status which is the highest category on the Saffir-Simpson scale.
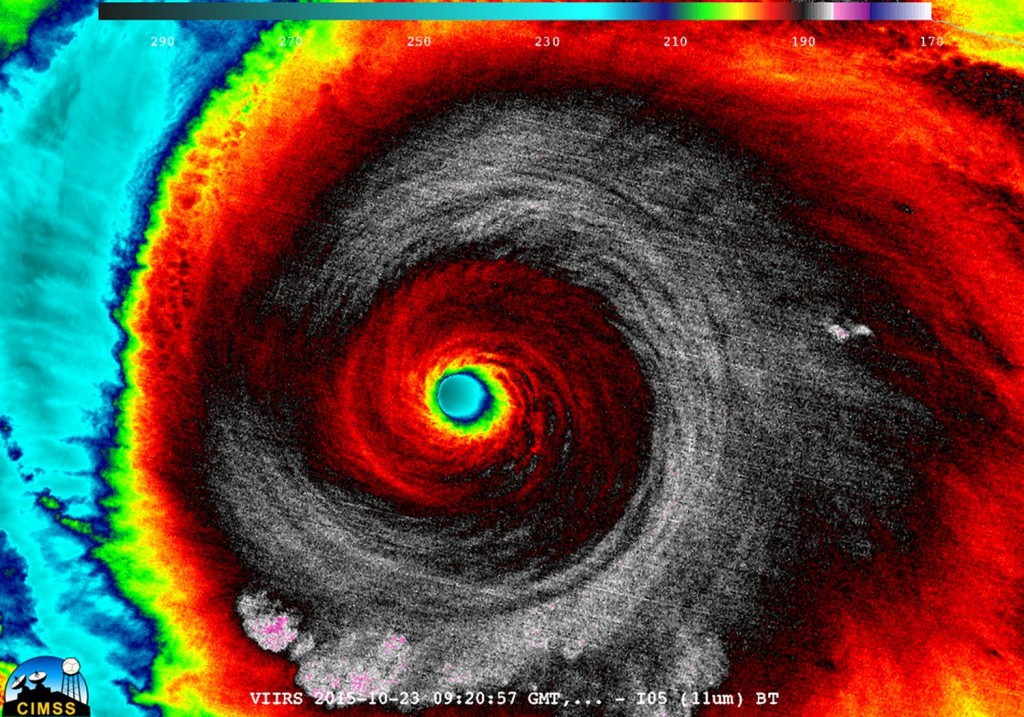
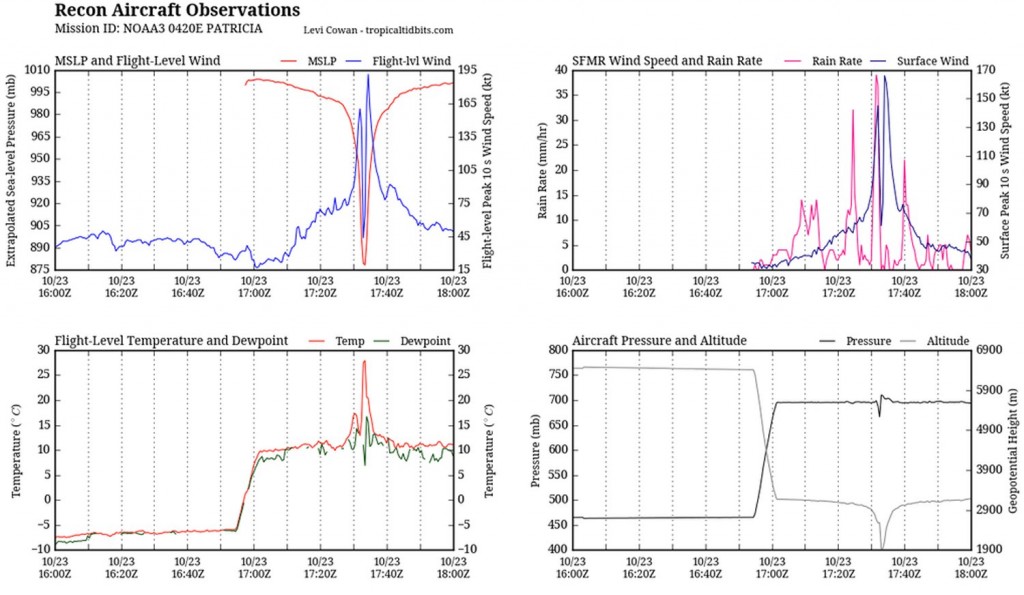
As it neared its peak early Friday morning, the hurricane hunters flew through the hurricane to sample the environment. The data collected was astonishing; a drop sonde had measured a surface pressure of 883mb with a 45kt surface wind. From this they extrapolated that the central pressure of Patricia was about 879mb at the time of the drop sonde, breaking another Western Hemisphere record for lowest pressure observed. Winds also peaked in Patricia around the same time, where sustained winds were 325km/h, with possible gusts up to 400km/h. Thankfully Patricia’s wind field did not extend very far from its core because it was a fairly compact inner core with pinhole eye – hurricane force winds only extended about 40km from the centre of the storm.
What’s it like flying into one of the strongest ever observed? Here’s a video of the Hurricane Hunters flying in Patricia:
Patricia made landfall as a category five hurricane southeast of Puerto Vallarta, near Cuixmala on Friday evening. Thankfully no deaths had been reported yet out of Mexico as of this morning but significant damage occurred along the coast near La Manzanilla which was both a result of storm surge and the strong winds. After encountering land and terrain Patricia’s inner core quickly collapsed and the system’s biggest threat has now shifted to heavy rainfall. Patricia’s moisture plume is expected to move northeast, helped by an upper level trough, across the Sierra Madres and into southeast Texas. A dangerous flash flooding event is ongoing this weekend in Texas with all the tropical moisture combined with a source of lift present.