A heat wave has taken hold across much of India in the past few weeks and will continue to do so before monsoon season arrives next week.
[map autofit=”1″ disable_scrollwheel=”1″] [pin]Bhubneshwar[/pin] [pin]Andhra Pradesh[/pin] [pin]Rajasthan[/pin] [/map]
A weak ridge aloft has allowed extreme heat to build into the region while tropical dewpoints over 25°C remain in place. With these temperatures and dewpoints combined, several locations in Eastern India, like Bhubneshwar, have seen humidex values above 55°C – signifying heat stroke is probable with any time spent outside. Not only that, but overnight lows stayed well above 30°C for several days in some regions, providing no relief to the residents. Additionaly, dust storms have been taking place across the drought stricken areas in the north. In Rajasthan, a dust storm killed seven people two weeks ago. Heat waves can be crushing to developing countries, such as India, resulting in exponentially more deaths and damages compared to first world countries as residents have limited access to clean drinking water to hydrate themselves, never mind air conditioned houses.
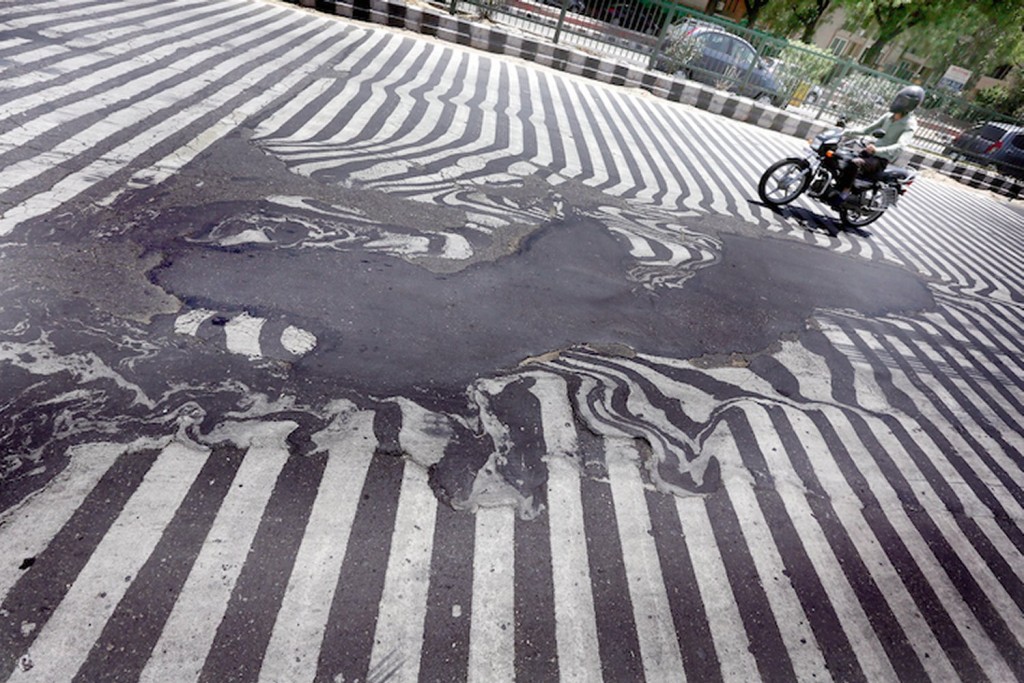

Over half of the deaths (1,334 deaths) associated with the heatwave came from the Andhra Pradesh province, while the most recent overall death tally reached 1,826 people. This, according to Jeff Masters of Weather Underground, is the fifth deadliest heat wave in world history since record keeping began and second deadliest to India (deadliest was 1998). Water shortages were the main problem leading to dehydration and heat stroke; to combat this, the country brought in water tankers and aid to over 4,000 towns in the hardest hit areas.
Help might be on the way however. The seasonal rains that India experiences, called monsoonal rains, are advancing northwestward towards the heat-stricken provinces. These will not only bring much needed moisture to the region, but also allow temperatures to drop well below what India has been experiencing past few weeks. The few weeks preceding the monsoonal season typically do bring heat waves and dry weather to India, but some years are harsher and last longer than others.