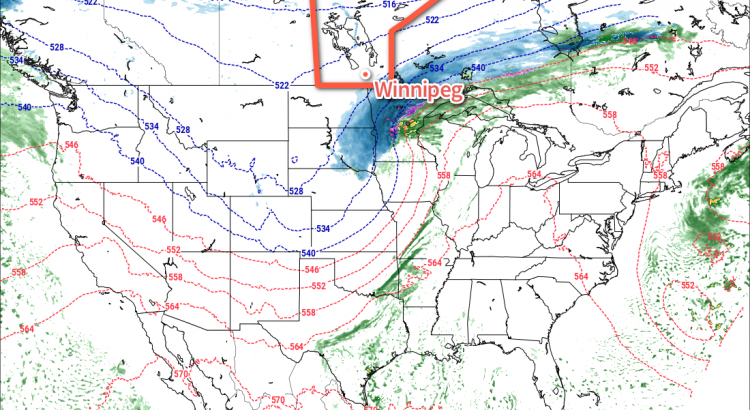
Will our first snowfall of the year come this week? That is the question that meteorologists are trying to answer as a complex weather system potentially brings accumulating snowfall to southern Manitoba tonight.
This Week
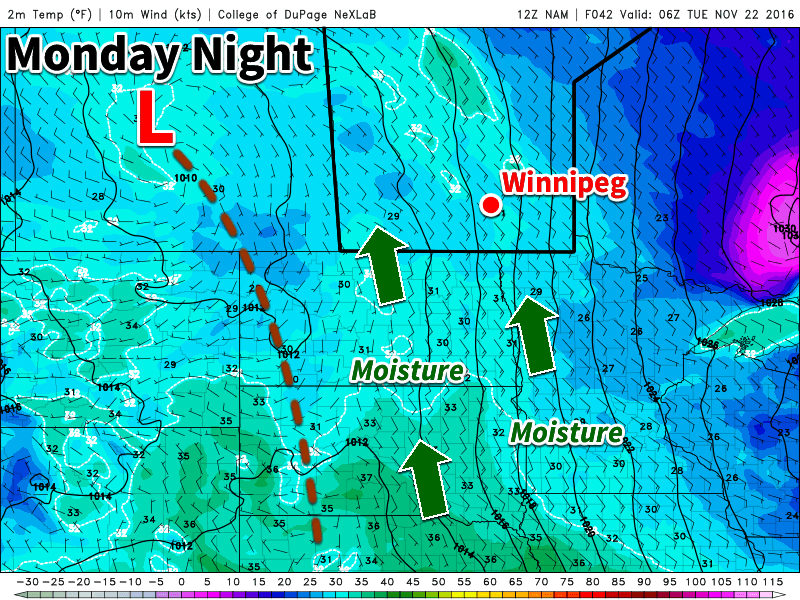
Today will start out cloudy and cool with temperatures hovering near the freezing mark. Change is coming, however, as a strong weather system moves off the mountains and begins to produce snow over the northern United States and southern Prairies. This is a complex system, with the strongest part well to our south over the midwestern US. A secondary part of this system will move across the southern Prairies and likely produce accumulating snowfall along part of its track. At this point it appears probable that snow will begin to develop over southern Manitoba on Monday night as moisture and lift begins to push into the region. The question is whether conditions will come together just right to produce significant snow over all of southern Manitoba, or whether the system will only begin to produce significant snow as it pushes into northwestern Ontario.
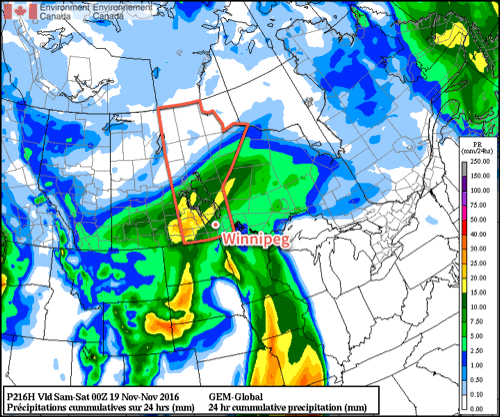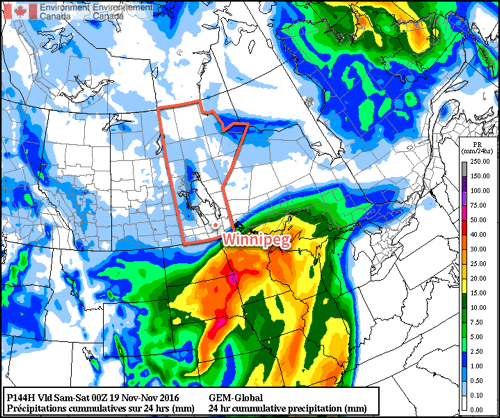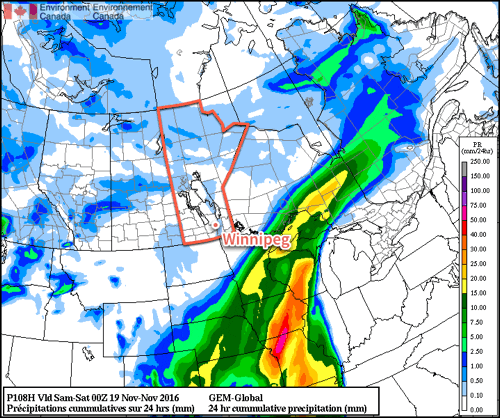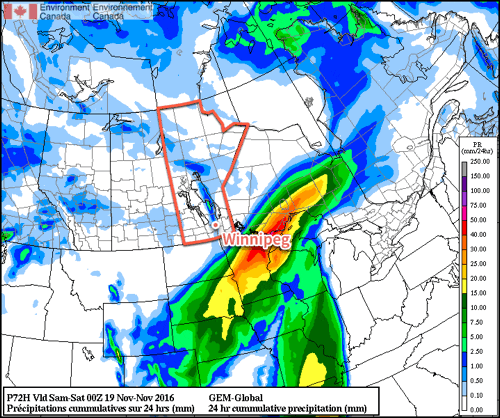
Weather model simulations generally begin to produce light snow over western Manitoba late on Monday afternoon, before the snowfall intensifies as it moves into the Red River Valley and southeastern Manitoba. This would likely result in 1-4 cm of snow over western Manitoba, 4-8 cm over the Red River Valley, and 5-10 cm over southeastern Manitoba. However, an alternative solution would have only minor snowfall (if any) over western Manitoba and the Red River Valley, with slight accumulations of 2-4 cm over southeastern Manitoba. The former solution is most favoured at this time, with about 5 cm expected in the Winnipeg region, with slightly higher amounts to the east and slightly lower amounts to the west. The most likely outcome may change as the system develops today, therefore you should stay tuned for more details.
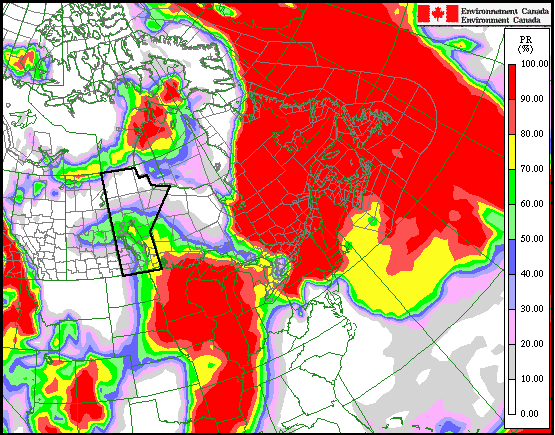
A map of the currently favoured snowfall outcome is shown below, showing the probability of at least 5 cm of snow; note that Winnipeg has a 70% chance of receiving at least 5 cm. Some blowing snow is possible, due to southeasterly winds of 30 km/h gusting to 50 km/h today, however blizzard conditions are definitely not expected. Winds will taper off by Tuesday, alleviating any blowing snow that does develop. The first major snowfall of the year is always one of the most challenging as drivers adapt to the changing conditions. Regardless of whether it snows tonight, this is probably a sign that you should get those winter tires on if you haven’t already!
Snow will taper off on Tuesday morning, should it materialize in the first place, leaving Tuesday with cloudy and cool conditions. Temperatures will once again sit near the freezing mark under mainly cloudy skies. The odd flurry is possible during the day, but generally quiet weather is expected. Winds will be light from the west.
A quiet weather day is expected on Wednesday as well, with mainly cloudy skies and just a lingering chance of flurries. Temperatures are likely to be around or just above zero. Winds will be northwesterly at 20-30 km/h.
Long Range
The long range outlook will be partly shaped by how much snow falls this week. If we manage to avoid major snow, it is likely that the remainder of November will remain generally warmer than normal. Because a blanket of snow on the ground reflects most of the incoming sunlight, it is more difficult for us to heat up during the day. The longer we avoid snow the longer we’re able to keep that darker, exposed soil which helps to absorb the limited sunlight that we do receive at this time of year. Should we receive significant snow with this upcoming system, we’ll likely see normal conditions through month’s end. Regardless of how much snow falls this week, this November is likely to end up as one of the warmest, if not the warmest, Novembers on record in Winnipeg.